september 2021

Global News & Analysis

5 New Security Executives Announced
Security executives on the move! Which industry leaders have recently begun new roles? Visit SecurityMagazine.com for the complete articles.



Malcolm Harkins — New Chief Security Officer at Epiphany Systems
Best known for his roles as the Chief Security and Trust Officer at Cylance and Vice President and Chief Security and Privacy Officer at Intel Corporation, Malcolm Harkins has spent his career managing risk, critical controls, privacy, cybersecurity and other compliance initiatives to better protect organizations from targeted attacks. Harkins is a Fellow with the Institute for Critical Infrastructure Technology, a non-partisan think-tank providing advice on cybersecurity to the House, Senate and various federal agencies. Congratulations! Image courtesy of Harkins

Kevin Koelmeyer – New Director of Cyber Security and Network Technologies at Infinet
Infinet Network Solutions has appointed former CISO of Somerville, Kevin Koelmeyer, as Director of Cyber Security and Network Technologies. Koelmeyer spent more than eight years in various senior technology and leadership roles at Somerville, of which his most recent position was Chief Information Security Officer (CISO). He built and managed the complete private cloud and security portfolio for Somerville’s Managed Service business.
He joins Infinet to lead and shape the organization’s security practice. He will be responsible for building and running a team of security professionals dedicated to designing, deploying and managing highly secure and scalable solutions. Congratulations! Image courtesy of Koelmeyer

Ross Honan – New Chief Information Security Officer at Drata
Ross Hosman is joining security and compliance automation company Drata as Chief Information Security Officer (CISO). In his new role, Hosman will be responsible for leading and growing Drata’s security program.
Before joining Drata, Hosman was the Head of Information Security at business intelligence company Sigma Computing and Recurly, a subscription platform. He also spent time as JPMorgan Chase’s Head of Cloud Security, building out an automation-focused security strategy. Before then, he held cloud security architect positions at VMware, Cisco and Expedia, providing him with comprehensive knowledge of the various cloud and hosting technologies. Congratulations! Image courtesy of Hosnan

Branville Bard Jr. – New Vice President of Public Safety at John Hopkins University
Branville Bard Jr. has been named Johns Hopkins University’s new Vice President for Public Safety. Bard will oversee security operations for all Johns Hopkins University and Johns Hopkins Medicine campuses and facilities worldwide, with the exception of the Applied Physics Laboratory.
Previously, Bard was Police Commissioner of Cambridge, Mass. Among many accomplishments during his tenure, he established the department’s family and social justice section to address the needs of vulnerable members of the community. He brought in the department’s first child psychologist to connect Cambridge youth and their families with mental health services and its first recovery coach to help address challenges presented by the opioid epidemic. Most recently, he launched a department-wide effort to proactively monitor data on police-citizen interactions for indications of possible racial profiling or biased policing and make that information available through near real-time updates to a public dashboard. Congratulations! Image courtesy of Bard

Rodney Chatman – New Vice President for Campus Safety at Brown University
Brown University appointed Rodney Chatman as its Vice President for Campus Safety. Chatman will serve as both Chief of Public Safety for Brown and as a senior leader who plays a critical role in promoting and sustaining a community in which students, faculty and staff are treated with respect and provided equal access to employment and educational resources in a setting defined by a commitment to well-being, safety and security.
Chatman is a campus safety and law enforcement leader with more than three decades of experience in municipal and higher education settings. Previously, he served as Police Chief of the University of Utah, and as police officer and then Captain at the University of Cincinnati, where he supervised a staff of close to 100 officers, along with security and emergency communications personnel. Congratulations! Image courtesy of Chatman
Disinformation Campaigns Against Brands are Flourishing Across Social Media
Disinformation, long used to spread and advance political ideologies, is now being used to damage Western corporations and economies, as reported by the Network Contagion Research Institute (NCRI) study, The Future of Disinformation Operations and the Coming War on Brands. The actors and methods employed to influence elections and spread falsehoods to polarize the United States electorate are now being leveraged for economic warfare. Moreover, an economic disinformation industry is emerging in which disinformation services are provided to domestic and foreign threat actors – a trend that the NCRI expects to continue.
To showcase the increase in disinformation campaigns targeting corporations, the NCRI first sought to quantify the scale and structure of the makeup of information operations and conspiracy for 5G technology, which has been targeted by Russia and China, as a means to discredit western 5G technology and promote their own technologies.
With assistance from partners, open-source platform analysis, and NCRI’s flagship platform, Pushshift, NCRI identified over 600,000 articles mentioning 5G published between January of 2019 and July of 2021, with roughly 70,000 from known sources of disinformation. Although the majority of articles mentioning 5G were from trusted sources (CNN, FOX Business, WSJ, etc.), the most cited articles mentioning 5G are from known Russian disinformation sources, including the entities, Global Research and RT, and non-state actors like Natural News and Children’s Health Defense, the NCRI say.
NCRI also analyzed over 17 million Twitter posts mentioning 5G between July of 2018 and July 2021. Starting with the COVID-19 pandemic, tweets mentioning 5G have included terms like stop5g, 5gkills, soros, gates, cancer, coronavirus and others. These developments showcase the flexibility of movements enabled by disinformation against brands, according to the NCRI.
Tommy / DigitalVision Vectors via Getty Images

Figure 1 — A partial time series analysis of multiple YouTube videos (top) and hashtags tweeted per minute (bottom) mentioned with 5G. Conspiracy theories and disinformation around 5G appear to emerge in synchrony across platforms and show steep increases in response to the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic. Image courtesy of the NCRI
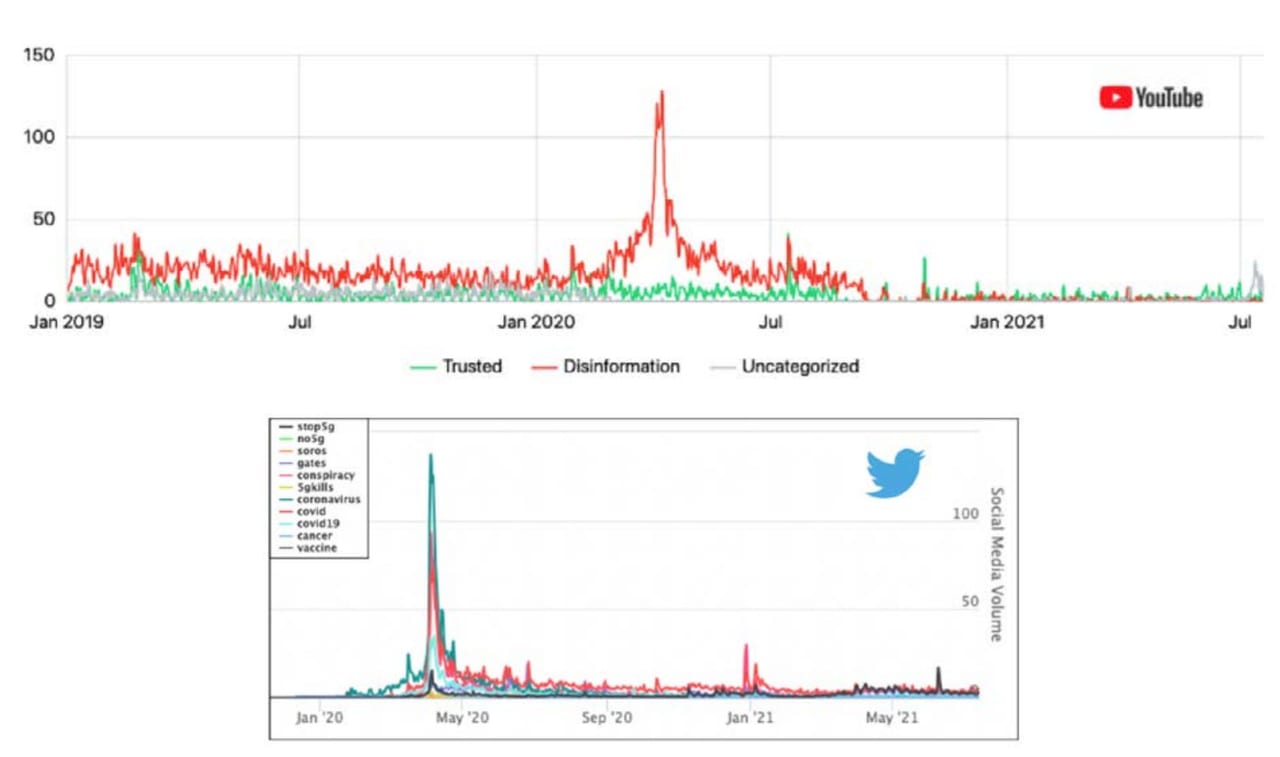
In this case, the onset of COVID-19 bolstered an unrelated, existing reservoir of disinformation around a technological dystopia, the NCRI found. In April and May of 2020, there were times when posts about 5G accompanied by these terms reached an average rate of 100 tweets per minute. Additionally, roughly 19,000 YouTube videos about 5G have accrued over 180 million views since January 1, 2019, and more than half of these videos amplified 5G conspiracy theories.
NCRI also examined anti-vaccination disinformation Russian campaigns that seek to degrade Western vaccine confidence and promote Russia’s Sputnik V vaccine. To gauge the information landscape related to American vaccines, NCRI identified over 4 million articles since January of 2020 mentioning American pharmaceutical companies involved in COVID-19 vaccine production (Moderna, Johnson & Johnson, and Pfizer). More than half a million are from known disinformation sources, and the content generated from known disinformation outlets generates the most engagement. NCRI also determined that sources connected to the Russian State (like Global Research and RT) and non-state actors have generated the most online articles on the topic, and those articles have been the most cited in other online articles.
To dissect how and when vaccine disinformation targeted specific brands in the social media sphere, NCRI collected over 8 million original tweets with the term “Pfizer” from early 2009 to July 2021 and analyzed the prevalence of conspiracy terms in conjunction with mentions of the word “Pfizer.”
Figure 2 — An analysis of original tweets per minute with the term “Pfizer” combined with terms common to known COVID-19 disinformation narratives showed a substantial surge (up to 100 times per/minute) in putative conspiracy theory and disinformation. These surges occurred in tandem with ongoing election challenges in the United States and phase 3 clinical results for the vaccine. Bottom: 5G conspiracy chatter is increasing in connection to Pfizer and other vaccine brands on Twitter. Image courtesy of the NCRI
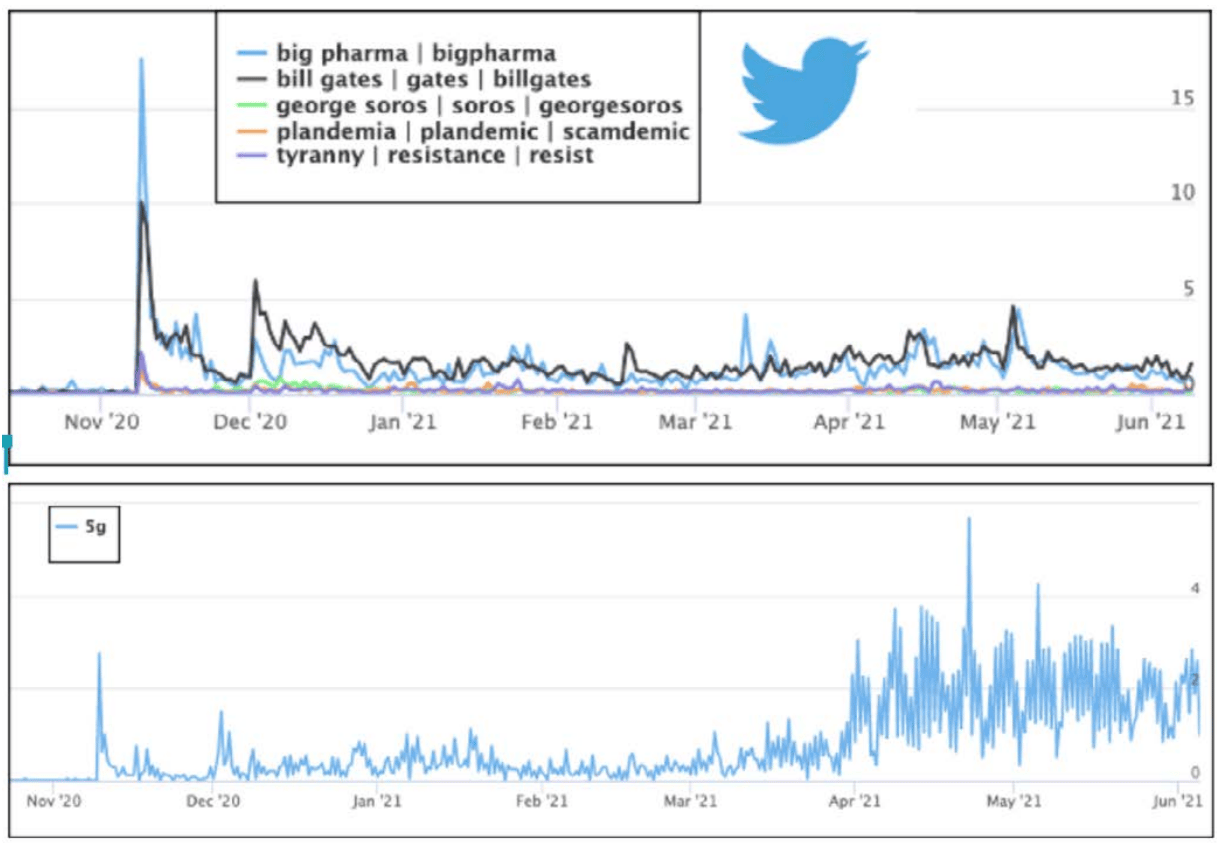
Interestingly, NCRI found substantial increases in the use of these terms during the contested election of 2020. The onset of a contested election, an unexpected source of a national political crisis, bolstered an unrelated, existing reservoir of disinformation against Pfizer and other vaccine brands. Finally, a notable trend in the gathered Pfizer data is an increased frequency of 5G comments (Figure 2, above).
Overall, the analysis shows how movements supported by disinformation operations can jointly impact multiple brands through unexpected combinations, the NCRI says. In fact, according to a recent Economist/YouGov poll, 1 in 5 Americans believe the U.S. government is using the COVID-19 vaccine to microchip the population. 5G is often a central theme in circulating vaccine microchip conspiracy theories.
NCRI researchers also examined disinformation in retail and the consumer economy at risk of targeted disinformation campaigns. In 2020, Wayfair, a furniture retailer, suffered negative publicity after a post on the r/conspiracy subreddit alleged that the company was at the center of a massive child trafficking ring. The conspiracy theory spread on social media channels such as Twitter, Facebook and TikTok.
The latest scope and sophistication of disinformation attacks orchestrated by foreign actors reveal a new security fault line that companies must anticipate as disinformation itself becomes a market commodity, the NCRI warns. This trend in disinformation poses unique risks to brand equity, employee relations, general corporate culture, customer and employee safety and consumer confidence; therefore, corporations must take an active role to find proactive mitigation strategies to counter disinformation operations.
The NCRI believes disinformation attacks will continue to proliferate, fueled by advances in artificial intelligence, deep fakes, progress in psychological profiling, and other combinations of technology and financial resources of sovereign nations.
Without a clear, outlined strategy to defend against disinformation, corporations are at severe risk. NCRI researchers recommend companies engage in a focused capability-building around disinformation defense and invest in in-house analyses and forecasting resources. Engaging topic experts in disinformation defense is also imperative to help corporations and leadership understand the web of actors and tactics in the world of brand and online disinformation.
Active Shooter Events, Threat or Harm to CEOs and Employees Have Occurred Due To Intelligence Failures
As COVID-19 vaccinations continue, companies embrace hybrid work, employees return to the office and the U.S. opens up, violence and physical threats to businesses are occurring at an alarming, record-high pace. These are some of the findings unveiled in the 2021 Mid-Year Outlook State of Protective Intelligence Report — The Escalating Physical Threat Landscape: A Clarion Call for Corporate Protective Intelligence, a new study commissioned by the Ontic Center for Protective Intelligence.
Of the physical threats that resulted in harm or death at companies in 2021, nearly half (49%) of respondents think most or almost all could have been avoided if cybersecurity and physical security intelligence were unified so threats could be shared and actioned by cross-functional teams.
In addition, 55% of physical security and IT leaders say their CEO believes in training employees so they are better prepared for potential workplace violence will create a culture of fear. Over one-quarter (26%) of those surveyed say their company has never addressed the potential for workplace violence, and employees would not know what to do if an active shooter entered their facilities.
Seventy-four percent of respondents agree that they anticipate significant conflicts between management and employees regarding health and safety protocols, as well as work-from-home policies when businesses reopen. Seventy-two percent agree that their company has experienced physical security threats after requiring employees to show proof of vaccination to return to the office.
Since the beginning of 2021, 58% of security and IT leaders say their company has received or investigated one physical threat (33%), between two and five physical threats (21%), or over six physical threats (4%) per week. Since the beginning of 2021, as a result of intelligence failures, respondents say the following incidents have occurred at their company:
An insider abused authorized cyber access that led to property theft or supply chain damage (34%);
An employee was threatened or harmed while working at company facilities (33%) or working remotely (28%);
A former employee threatened or harmed current employees (25%);
CEO and family members received threats or were harmed when working from their private residence or while traveling (24%);
An active shooter event occurred at one of the company’s locations (18%).
“Pent up economic and political frustrations marked January 6 by the Capitol riot are being unleashed after months of limited in-person interactions, mass shootings have skyrocketed, and companies are experiencing an increase in physical threats as compared to the beginning of 2021,” says Fred Burton, Executive Director of the Ontic Center for Protective Intelligence. “And yet, as our study found, even as physical threats increasingly originate in the cyber world, CEOs are reluctant to believe their companies could be targets.”
Burton adds, “As the crippling of critical supply chains and infrastructure by cybercriminals earlier this year demonstrated, to keep all aspects of their business safe, with great urgency, companies must fund, integrate and unify cybersecurity and physical security intelligence, assessment, mitigation and operations across the enterprise.”
Finally, 91% of respondents agree physical security teams needs a technology-driven industry standard for actively identifying, investigating, assessing, monitoring and managing physical security threats. In addition, 87% agree that now is the best time to invest in physical security digital transformation to advance security effectiveness and mitigate violent threats is necessary for the future of their company.
The findings illustrate that an always-on, security-driven approach to safety can effectively advance business continuity and reduce threats to staff, employees and visitors in today’s escalating physical threat landscape.
Ignatiev / E+ via Getty Images

Access Control, Site Security and Occupant Safety Are Key Focus Areas for Education Leaders
In a new report, 93% of surveyed facility managers within the education vertical say they have experienced at least one emergency incident stemming from infrastructure malfunction during the last 12 months, and 43% report a physical site or cybersecurity breach in that time. The report, Rethinking Education Facilities as Digital Entities, the second in Honeywell’s 2021 Building Trends series, presents the assessments, challenges and priorities of education facility managers in the United States, Germany and China.
The report highlights current conditions in school facilities, spanning both geographical regions and education levels — from pre-kindergarten through primary, secondary, trade schools, colleges and universities. Facility managers voiced their concerns about physical infrastructure and plan to invest in digital infrastructure to enhance site security, occupant safety, building health and emergency response.
Nearly half (45%) say they rank site security (video surveillance and campus access control) or fire and life safety systems as top priorities over the next 12 to 18 months. The survey results from education facility managers across all three countries underscore five key themes:
Security and safety are top priorities. Half (52%) of respondents rank site security as a top priority, including 34% who say improving site security through video surveillance, access control and asset security systems is their top priority over the next 12 to 18 months. When asked about their facility concerns, a majority of respondents list physical site security and access control (77%); communicating important information to staff, students and parents (76%); identifying proper security and intrusion issues (73%); and air filtration and contaminant reduction (74%).
Healthy buildings remain a focus area. Compared to their pre-pandemic priorities, 63% of surveyed education facility managers are now more willing to invest in healthy building solutions. A majority (58%) of respondents list a healthy building as a top priority now, and 60% say it will remain a top priority beyond COVID-19. As for which elements of a healthy building they consider most important, 49% of respondents say improving indoor air quality and 47% rate real-time access to building health metrics as critical.
Education facilities deal with infrastructure and budgeting challenges. Surveyed education facility managers experience more challenges — and have more difficulty addressing them — than their counterparts in the healthcare, data center or commercial real estate sectors. Nearly a fourth (23%) cite at least one emergency stemming from fire, smoke, gas, overheating or water over the past 12 months, and 56% have had to deal with an incident related to less threatening but still disruptive infrastructure malfunctions such as a power or network outage. More than 7 in 10 (71%) say budgeting for upgrades or new technology solutions is often difficult. Supposing they can secure the budget, 72% say implementing the upgrades can be challenging. Other top areas for improvement include creating a healthier, safer environment for occupants (65%); minimizing downtime or disruptions (71%); and achieving or increasing energy efficiency (71%).
Digital transformation compounds educators’ infrastructure needs. More than 7 in 10 (71%) respondents find it challenging to keep pace with technological changes in their facility systems. Asked whether they currently have digitally enabled health, safety or security technology, fewer than 4 in 10 respondents answer affirmatively to any of the following: gunshot detection (15%); an app that provides real-time building health data (27%); integrated lighting that improves occupant productivity (27%); software that provides insight into fire systems (33%); remote building management (35%); or aspirating smoke detection (34%).
A smart school is key to a healthier, safer and more secure school. Across all three countries, 64% of respondents are more likely to invest in intelligent building solutions today than they were pre-pandemic, and 56% say the ability to manage all building systems through a single platform that provides unified data and insights is one of the most important aspects of a smart building. As for specific digital solutions, a majority are likely to invest in at least one of the following in the next 12 to 18 months: an app that provides real-time building health information (37%); software to provide better access and insight into fire systems (35%); security products with increased cybersecurity protocols (34%); contactless building entry (31%); or remote building management (27%).
dlewis33 / E+ via Getty Images

SEPTEMBER 2021 | securitymagazine.com




